Anaerobic digestion is widely applied to sewage sludge and other organic residuals to stabilize the substrate and capture some of its energetic value via the production of biogas. By combining anaerobic digestion with nutrient recovery technologies, both energy and nutrients could be recovered. Struvite precipitation and ammonia stripping are two of the most mature technologies to recover phosphorus and nitrogen from streams such as the liquid fraction of anaerobic digestate. But how effective are these two processes in terms of nutrient recovery?
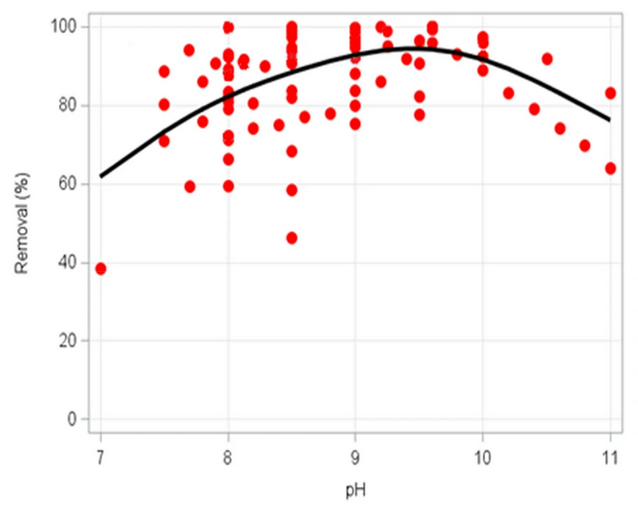
In a paper published in Environmental Evidence, Lorick et al. (2020) present a systematic review of the effectiveness of struvite precipitation and ammonia stripping for the recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from anaerobic digestate. The review includes 30 studies on struvite precipitation and 8 studies on ammonia stripping. While both pH and the Mg:PO4 ratio were found to have a clear influence on the effectiveness of the struvite precipitation process, these two factors alone are insufficient to accurately predict recovery efficiency. As for ammonia stripping, no conclusions could be drawn to the small size and the heterogeneity of the evidence base.
Lorick D, Macura B, Ahlström M, Grimvall A, Harder R (2020). Effectiveness of struvite precipitation and ammonia stripping for recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from anaerobic digestate: a systematic review. In Environmental Evidence. DOI: 10.1186/s13750-020-00211-x.
Contact: Robin Harder