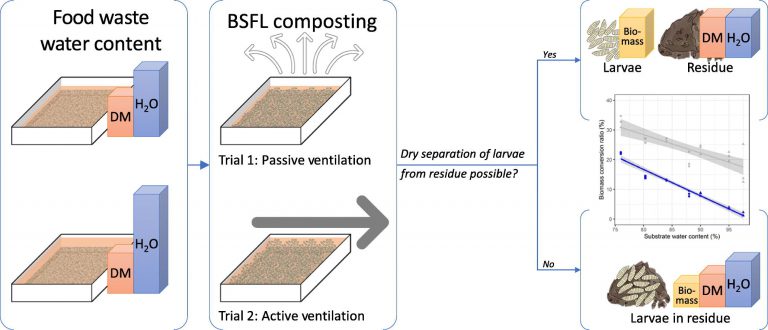
Our latest publication on BSFL composting entitled Process efficiency and ventilation requirement in black soldier fly larvae composting of substrates with high water content has been recently published in Science of the Total Environment. In this study we investigated the impact on increasing substrate water content on the process efficiency in black soldier fly larvae composting. We used the gathered data to make a model predicting the required ventilation for achieving a residue dry enough to allow for dry separation of larvae from treatment residue at the end of the composting. In contrast to what other studies have found, we fund that it is possible to BSFL compost substrates with water content 80 – 90 % and dry separate the larvae from the residue. For substrates with water content >90% it was more difficult, as the process efficiency decreased greatly, while the ventilation requirement increased.
Lalander, C., Ermolaev, E., Wiklicky, V., & Vinnerås, B. (2020). Process efficiency and ventilation requirement in black soldier fly larvae composting of substrates with high water content. Science of The Total Environment, Volume 729, 10 August 2020, 138968.
Contact: Cecilia Lalander
