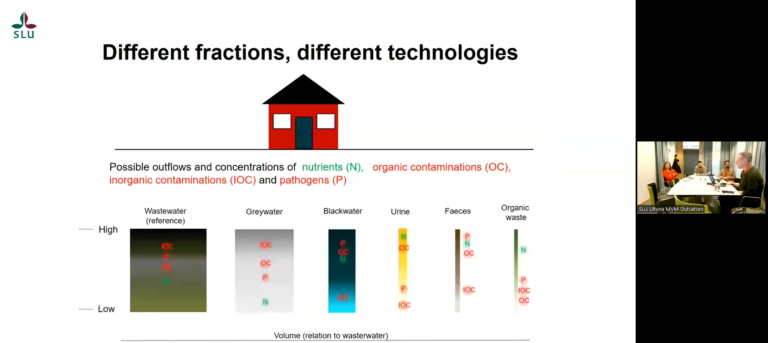
There is a growing trend for nutrient recovery from wastewater as part of the transition to a circular economy. Most nutrients in household wastewater originate from urine and one way to facilitate reuse of these nutrients is to concentrate the urine into fertilizer products. Urine concentration technologies are still in the development phase and not implemented at scale. The aim of this study was to provide guidance to technology developers and policymakers by assessing the environmental and societal impacts of urine concentration technologies. In particular, it includes practical aspects such as worker safety, space availability and local fertilizer needs that have not been included in previous studies.
“Although many nutrient recovery technologies are not yet mature, it is good to evaluate them now. First to understand if they contribute to the sustainability that we want to achieve and then to identify improvement opportunities within the technology. It gives us guidance both for technology development and our strategic system planning.” says Jennifer McConville, one of the researchers behind the study.
Future scenarios on implementing three different urine concentration technologies (alkaline dehydration, nitrification-distillation, ion-exchange with struvite precipitation) in a planned residential area in Malmö, Sweden, were developed. The technologies were evaluated using multi-criteria assessment (MCA), with environment, technical, economic and health sustainability criteria derived from the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It was found that all urine concentration technologies performed well against many of the sustainability criteria examined and can contribute to achieving SDGs, especially regarding nitrogen recovery. Specific areas for further development were identified for each technology. In particular:

- Alkaline urine dehydration requires optimization of energy demand, to reduce the energy consumption and costs.
- Nitrification-distillation requires optimization of the nitrification rate and matching it to the distillation capacity, which can reduce space requirements and costs. Attention should also be given to risk factors for workers.
- Ion-exchange with struvite precipitation can be improved with respect to costs and risk for workers, in particular regarding use of sulphuric acid in regeneration of the ion-exchanger.
An impact assessment on scaling up demonstrated that nitrogen emissions to surface water were significantly reduced when more than 60% of urine in Malmö city was subjected to urine concentration. Nitrogen and phosphorus recovered from recycling only 15–30% of urine in Malmö could supply 50% of Malmö municipality’s fertilizer demand.

In the study, the researchers also tested the potential for more large-scale production of fertilizer through a scenario where the technology was scaled up to cover larger parts of Malmö. An up-scaling resulted in significantly lower emissions of nitrogen to the surrounding surface water and if 15 – 30% of the urine in Malmö is collected and concentrated, 50% of the municipality’s need for fertilization can be met.
Read the follow article here:
Gunnarsson, Matilda, Cecilia Lalander, and Jennifer R. McConville. “Estimating environmental and societal impacts from scaling up urine concentration technologies.” Journal of Cleaner Production 382 (2023): 135194.
 t.
t.
 Erika Francisco is originally from Brazil, where she completed a bachelor degree in Environmental Sanitation and a PhD in Chemical Engineering, specifically focusing on biorefineries for reuse and valuation of wastewater for the production of bio-products from microalgae. She has worked as a university lecturer in the Environmental Engineering Department at University of Passo Fundo for three years and as a Postdoctoral Researcher in the project “Food-Energy-Water Nexus Governance” bythe University of Campinas and Belmont Forum.
Erika Francisco is originally from Brazil, where she completed a bachelor degree in Environmental Sanitation and a PhD in Chemical Engineering, specifically focusing on biorefineries for reuse and valuation of wastewater for the production of bio-products from microalgae. She has worked as a university lecturer in the Environmental Engineering Department at University of Passo Fundo for three years and as a Postdoctoral Researcher in the project “Food-Energy-Water Nexus Governance” bythe University of Campinas and Belmont Forum.