By: Aida Bargues Tobella, Postdoctor at the Department of Forest Ecology and Management; Tropical Forestry and Land Use Management Unit
Land degradation is a major problem in the tropics. Such degradation entails a decline in the capacity of the land to produce and provide ecosystem goods and services, with negative impacts for human livelihoods, food security and the environment at large.
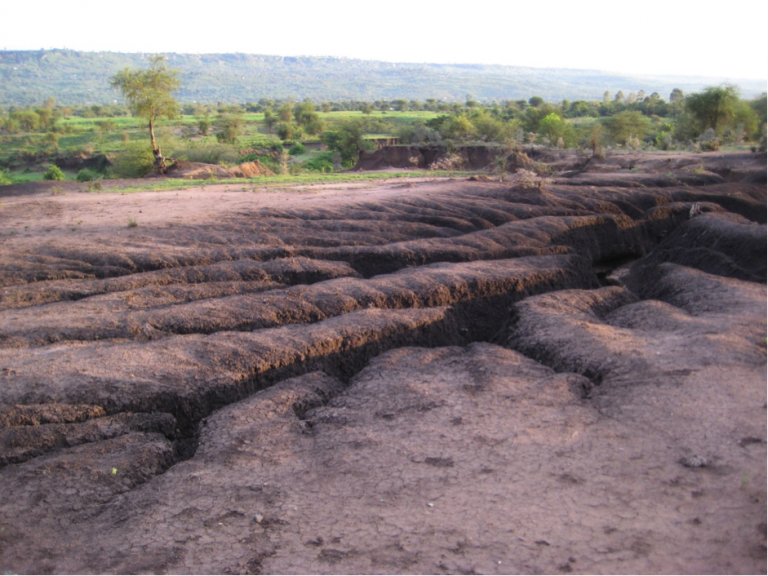

The establishment of trees on degraded lands is considered a fundamental tool in landscape restoration. Establishing trees is about more than just planting trees, and can include assisted natural regeneration (ANR) of forests, farmer-managed natural regeneration or direct seeding among other techniques. Similarly, the concept of landscape restoration is not limited to re-establishing lost forests and should be seen on a broader perspective, taking into consideration, for instance, the incorporation of trees into farming systems (agroforestry).

The potential benefits from tree-based restoration include enhanced water quality, biodiversity, carbon sequestration, soil fertility, and food and nutrition security. But, how much do we know about tree-based restoration? What are the trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services from trees? What management practices and tree traits contribute most to promote specific ecosystem services? As we enter the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, answering such questions is pressing.

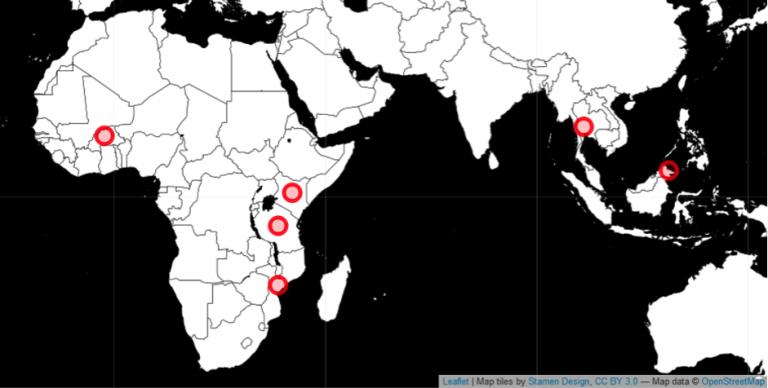
In the research group on Tropical Forestry and Land Use Management at the Department of Forest Ecology and Management in SLU, we work towards advancing our understanding of tree-based restoration of degraded landscapes in the tropics. Currently, we have projects in six countries across the global tropics: Malaysia, Thailand, Kenya, Burkina Faso, Tanzania and Mozambique.
Rainforest degradation and restoration
The group has been doing research on rainforest degradation and restoration in Borneo for over 35 years. The INIKEA Sow-a-Seed rainforest restoration project in the Malaysian state of Sabah is a collaboration between the Sabah Foundation, SLU and the Swedish furniture company IKEA andit is unique in that it is one of the largest and most successful tropical rainforest restoration projects in the world. Since the startof the project in 1998, we have planted more than three millionseedlings, consisting of ca. 80 different indigenous tree species, and roughly14,000 ha of forest have been restored with assisted natural regeneration and enrichment plantings.
In connection with the project, we have established a number of scientific experiments:
- In the SUAS experiment, established already in 1992, we aim to develop silvicultural methods that make management of natural forests environmentally and economically sustainable.
- In our three different species/genetic common gardens we seek to advance the present lack of knowledge on the economic and environmental values of indigenous species. Here we also study the importance of genetic variation in traits within and among species.
- In the Rainforest Restoration Experiment,we have established 84 plots in various forest types to evaluate where each of our four different approaches of restoration is most appropriate; 1) Passive protection; 2) ANR; 3) ANR with line planting and 4) ANR with gap-cluster planting.
- In our permanent sampling plots inside the restoration area and surrounding landscape of large-scale oil palm and industrial tree plantations as well as undisturbed protected forests, we are evaluating ecosystem values, such as economic value, carbon sequestration, water quality and biodiversity among these land-use systems.
These long-term forest management experiments in northern Borneo provide many opportunities for research. In the project Balancing production and ecosystem services from degraded tropical rainforests to aid the transition to a more sustainable bio-based economy, we are using data from these experiments to quantifybiomass production and a range of ecosystem services across multiple spatial and temporal scales. Using a multi-disciplinary approach, including aspects of economics, social science, silviculture, plant ecophysiology, ecology, human health,and biogeochemistry, we aim to identify sustainable management practices that can maximize the production of raw materials while at the same time minimizing adverseenvironmental impacts. Using this holistic approach, the overall objective is to obtain and communicate novel information to scientists, private, and government stakeholders about trade-offs between biomass production and ecosystem services to aid the transition to a sustainable bio-based economy.
Rainforest vulnerability to climatic water stress
The frequency and intensity of drought events are predicted to increase in tropical monsoon forests of Southeast Asia, ecosystems that are known to be biodiversity hotspots and a persistent carbon sink in the global carbon cycle. Such increases could drive rapid and large-scale shifts in forest structure and species composition as well as cause dramatic decreases in the amount of carbon stored by these tropical forests. We have recently started a research project thatbrings together scientists from Thailand, France,and Sweden, to assess the vulnerability of mature and secondary forests to climatic water stress. Such information is crucial to more accurately predicted how future climate change wouldaffect the cycling of carbon and water in tropical forested ecosystems.
Trees and water in African tropical drylands
Another leading research topic of the group is how we can use trees to improve soil and water resources in African tropical drylands. Our previous research in the seasonally dry tropics indicates that an intermediate tree cover can maximize groundwater recharge, which is contrary to the predominant scientific view that more trees always lead to less water. But, under what specific conditions can more trees improve groundwater recharge? Together with scientists from the World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF), the Norwegian University of Life Sciences and Wageningen University, we are evaluating the extent of the optimum tree cover theoryacross African tropical drylands. To do this, we are primarily using data from the network of Land Degradation Surveillance Framework (LDSF) sites, which is hosted at ICRAF. To date, the LDSF has been employed in over 200 sites across the global tropics and therefore constitutes a unique dataset to test this theory. The overall aim of the project is to provide evidence to inform better land-use policies in African tropical drylands and identify management options that can increase groundwater resources.
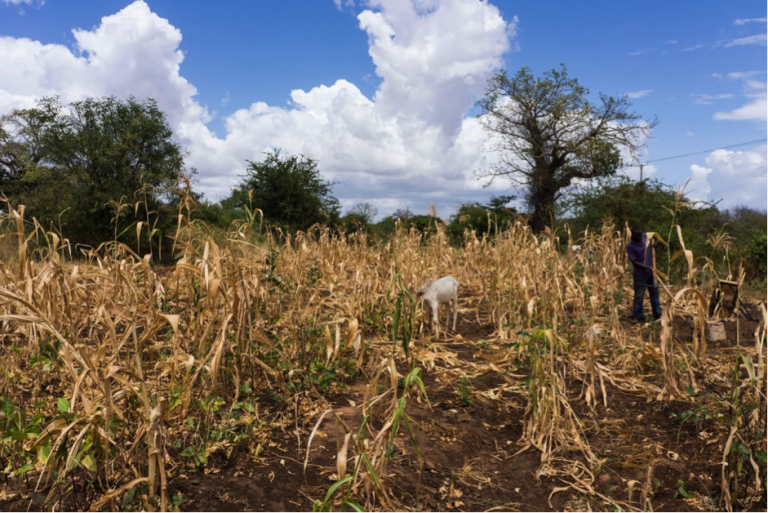


Courses
Are you interested in these questios and want to learn more about tropical forestry and land-use management? At the moment we offer two courses within this field:
- Sustainable Forestry and Land-use Management in the Tropics for MSc students
- Forest Management, Land Use Change and Ecosystem Services in Degraded Tropical Landscapesfor PhD students


Who we are
Ulrik Ilstedt, associate professor; ulrik.ilstedt@slu.se
Gert Nyberg, associate professor; gert.nyberg@slu.se
Niles Hasselquist, associate professor; niles.hasselquist@slu.se
Rosa Goodman,associate senior lecturer; rosa.goodman@slu.se
Aida Bargues Tobella, postdoc; aida.bargues.tobella@slu.se
Daniel Lussetti, postdoc; daniel.lusetti@slu.se



